
What You Need to Know about Direct Vent Fireplaces
Most factory-built or manufactured gas fireplaces today are designed as direct-vent units. These energy-efficient venting systems have replaced more outdated designs, and are the primary style of fireplace installed in homes built in the last 20 to 30 years. These fireplaces are also perfect for use during a remodel or room addition. Think a direct-vent fireplace might be right for your home? Read on to learn more about these great products.
How Does a Direct Vent Fireplace Work?

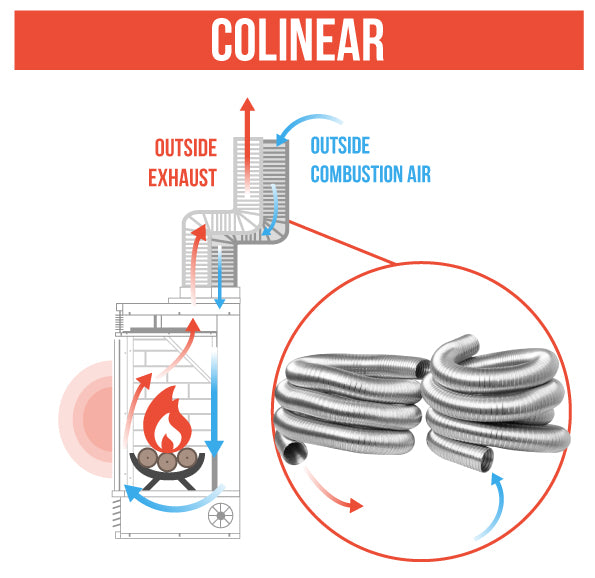
Direct-vent fireplaces are fully contained fireplace units designed to draw in fresh air and expel combustion byproducts outside the structure. There are two main types of direct vent fireplace: coaxial and colinear. The first type, coaxial, consists of a pipe within a pipe, where the outer portion serves as an intake and exhaust exits through the inner tube. The second type of direct vent fireplace, colinear, consists of two pipes in line with one serving as a dedicated intake pipe and the other serving as a dedicated exhaust pipe.
Both primary styles of direct venting provide several benefits. Each avoids issues such as oxygen starvation and poor draft. Additionally, these fireplaces perform well under strict energy efficiency requirements.
Primary Features of a Direct Vent Fireplace
Improved Venting Design

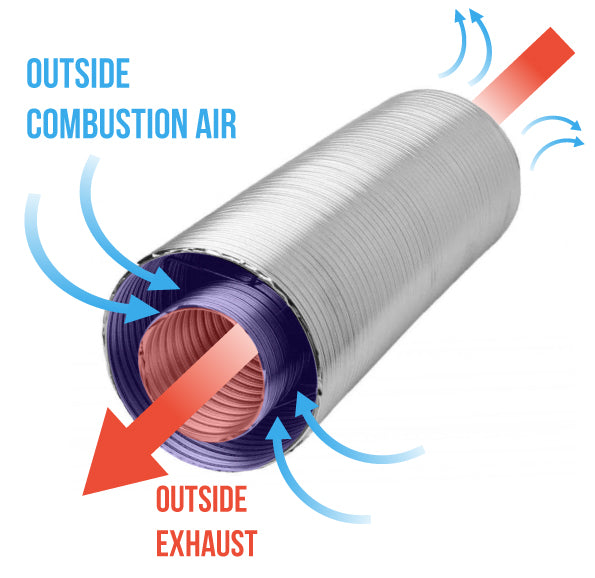
Direct-vent fireplaces feature a sealed intake and exhaust. These units draw air in from outside the home, exhaust to the outside and radiate heat to the inside for an efficient design. Unlike traditional fireplaces, direct-vent fireplaces are not impacted as much by drafts and air pressure changes.
Venting Considerations
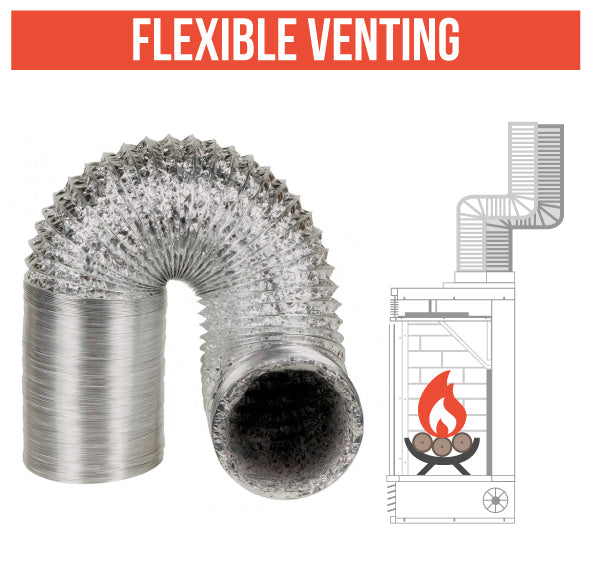


Direct-vent metal ventilation ducts can be rigid or flexible depending on the needs of the installation as well as the manufacturer's guidelines. These vents can be routed through an exterior wall, out the roof or power-vented to go around obstacles or long distances. Additionally, no masonry chimney is required in a direct vent installation but clearances to combustibles must be maintained based on the manufacturer’s specifications.
Electrical Considerations
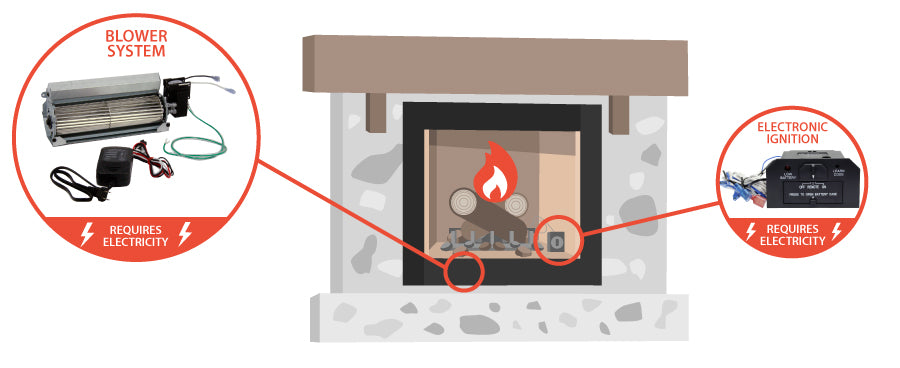
Most direct-vent fireplaces are simply gas-powered and do not require electricity for basic operation. A standing pilot light combined with a simple and reliable millivolt valve system create a safe design. In newer or more advanced direct-vent fireplaces, a source of electricity may be required for features such as blower fans, lights or electronic ignition systems. In addition, most new units feature an Intermittent Pilot Ignition (or IPI) that uses electricity to spark the pilot light and ignite the unit. Then, after use, the pilot shuts down as well to save fuel costs as well as extinguish any standing flame.
How to Install a Direct Vent Fireplace
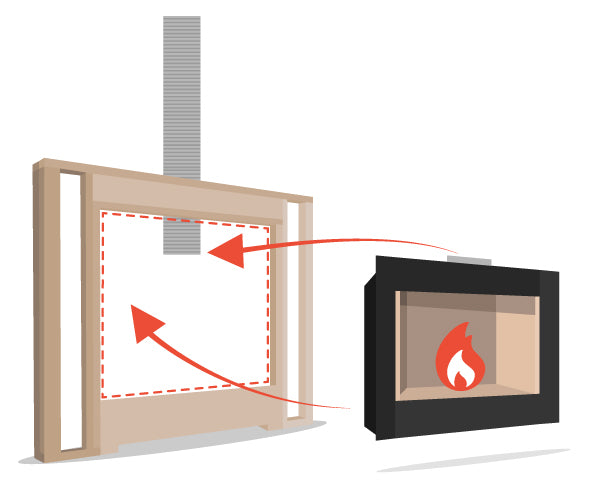
Direct-vent fireplace installations should be done by a trained professional to ensure safe operation. Always check appliance manufacturer information for direct vent configurations. It is important to note every fireplace will have designated venting systems that must be used in order to ensure proper installation. Again, a certified installer will simplify this process, but each fireplace's manual will have specifications and charts covering venting options. While direct-vent systems are simple and straightforward, we know that every installation can have its own variables which can create unique challenges during installation; all the more reason to consult both us and a certified installer.
Are Direct Vent Fireplaces Energy Efficient?
Direct-vent fireplaces are energy efficient for several reasons, namely they are self-sufficient heating appliances, not drawing air and heat from the room.. For this reason, some of these units operate with up to 70 percent efficiency. These fireplaces are also much more efficient than traditional or decorative vented gas logs, which lose the majority of their heat through the chimney.
How Much Does It Cost to Run a Direct Vent Fireplace?

Typically, fireplaces are measured in terms of BTU (British Thermal Units) per hour. Natural gas users are typically billed in therms, which are equal to 100,000 BTU. Knowing this, many direct-vent fireplaces are rated for between 20,000 and 30,000 BTU/hour, which would equate to about 1/5 to 1/3 of a therm for natural gas or gallon of propane.
As of November 2019, data collected from the U.S. government estimates the average cost per therm of natural gas is about $1.06. This puts the cost of using natural gas around 20 to 35 cents per hour. For propane users, propane is typically measured by the gallon, which is about 91,000 BTU total. Again, using data provided by the U.S. government, bulk LP costs about $2.00-$2.50 per gallon measured for 2019. That puts the cost of the fireplace units at 40 to 83 cents per hour.
Looking to Add a Direct Vent Fireplace to your Home?
Call us today to speak with one of our fireplace experts. They can walk you through the buying process to ensure you find the right product for your home. Contact us for more information.
